Sexual Health from a Physical Stand Point
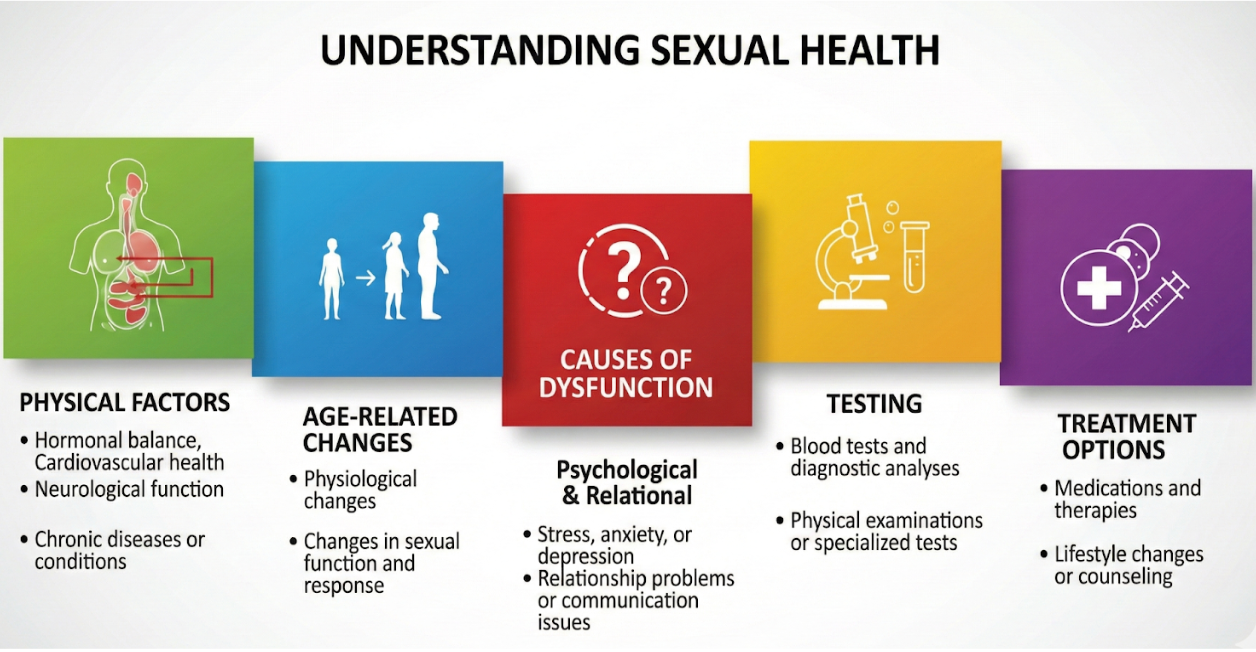
Sexual health is an important part of overall well-being for both men and women. From a medical perspective, healthy sexual function depends on a combination of hormonal balance, proper blood flow, nerve function, and psychological readiness. When any of these systems are disrupted, sexual dysfunction may occur. This blog provides a focused overview of the physical basis of sexual health, common causes of dysfunction, age-related changes, diagnostic tests, and evidence based treatments.
1. What Is Sexual Health From a Physical Standpoint?
For Men
Sexual health depends on:
- Adequate blood flow to the penis
- Healthy nerve signaling between brain, pelvic nerves, and penile tissue
- Balanced hormones, especially testosterone
- Functional penile tissue, including smooth muscle and vascular structures
These systems work together to allow libido, erection, ejaculation, and orgasm.
For Women
Sexual health relies on:
- Adequate blood flow to the clitoris, vaginal walls, and pelvic tissues
- Vaginal lubrication and tissue elasticity
- Balanced hormones (estrogen, progesterone, testosterone)
- Pelvic nerve function
- Healthy pelvic floor muscles
These factors support desire, arousal, lubrication, and orgasm.
2. Pathophysiological Changes That Cause Sexual Dysfunction
Common Causes in Men
- Vascular disease (hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes) → reduced penile blood flow
- Low testosterone → low libido, weak erections
- Neurologic issues (diabetic neuropathy, spinal injury)
- Medications (SSRIs, antihypertensives, opioids)
- Prostate surgery or pelvic surgery
- Psychological factors (anxiety, relationship issues)
Common Causes in Women
- Low estrogen → vaginal dryness, pain with intercourse
- Low testosterone → decreased libido
- Pelvic floor dysfunction → pain, difficulty with orgasm
- Reduced blood flow due to vascular disease
- Chronic illnesses (diabetes, autoimmune disease)
- Medications (antidepressants, antihistamines)
- Menopause-related changes affecting lubrication and tissue elasticity
3. Normal Age Related Changes
Men
- Gradual decline in testosterone after age 30
- Longer time to achieve erection or orgasm
- Less rigid erections
- Longer refractory period (time between erections)
Women
- Perimenopause and menopause cause major hormonal shifts
- Vaginal dryness and thinning of tissues
- Decreased elasticity and lubrication
- Lower libido due to hormonal decline
- Changes in pelvic floor strength
These changes are normal but may be managed with treatment when they affect quality of life.
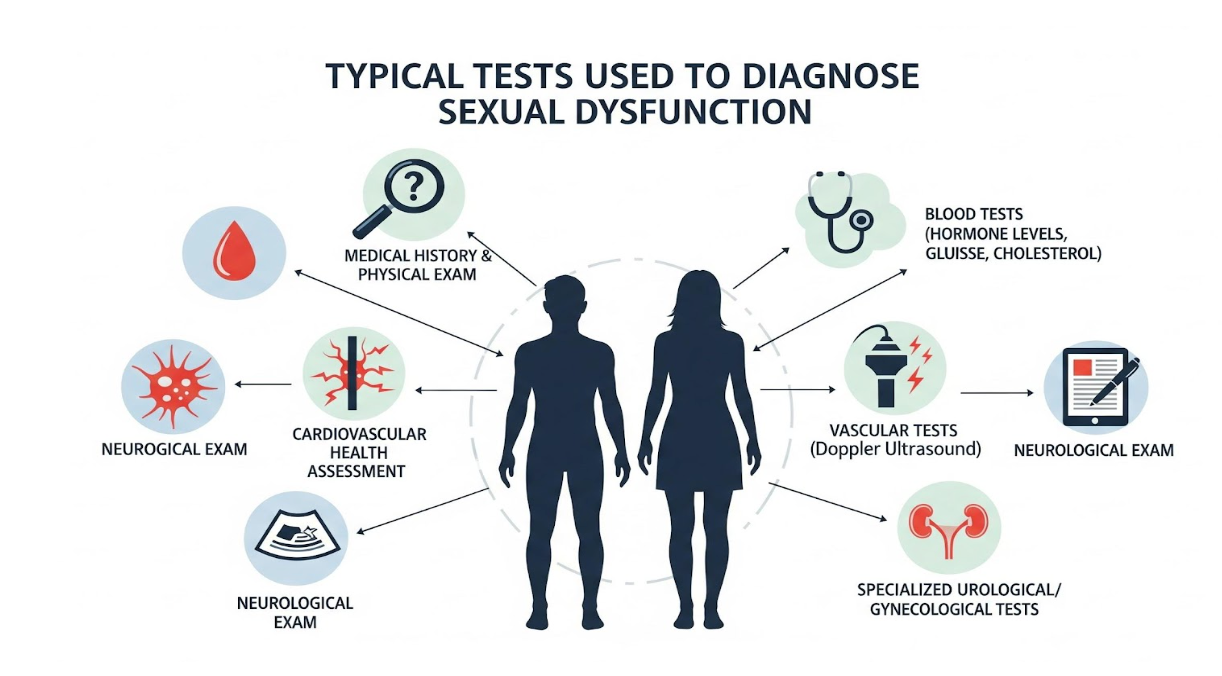
4. Typical Tests Used to Diagnose Sexual Dysfunction
Healthcare providers may order:
For Men
- Hormone tests: Total testosterone, free testosterone, LH, prolactin
- Diabetes screening: A1C, fasting glucose
- Lipid panel (vascular health)
- Thyroid function tests
Penile Doppler ultrasound if vascular issues are suspected
For Women
- Hormone tests: Estrogen (estradiol), progesterone, testosterone, FSH, LH
- Thyroid tests
- A1C and glucose
Pelvic exam to assess tissues - Pelvic ultrasound for structural abnormalities
- Evaluation of vaginal pH or infections if dryness/pain is present
For Both
- Medication review
- Mental health screening if needed
- Cardiovascular risk assessment
5. Evidence-Based Medical Treatments for Sexual Dysfunction
Treatments for Men
- PDE-5 inhibitors: Sildenafil (Viagra), Tadalafil (Cialis)
- Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) for confirmed low testosterone
- Vacuum erection devices
- Penile injections (alprostadil)
- Lifestyle and health management: exercise, weight loss, diabetes control
- Psychosexual therapy when psychological factors play a role
Treatments for Women
- Hormone therapy
- Estrogen therapy (oral, patch, or vaginal)
- Vaginal estrogen cream or tablets for dryness
- Testosterone therapy (in select cases for low libido)
- Non-hormonal treatments
- Lubricants and moisturizers
- Pelvic floor physical therapy
- FDA-approved medication for low libido (e.g., flibanserin, bremelanotide)
- Treatments for pain
- Vaginal laser therapy (in select cases)
- Topical lidocaine for vulvodynia
- Treatment of infections or pelvic floor disorders
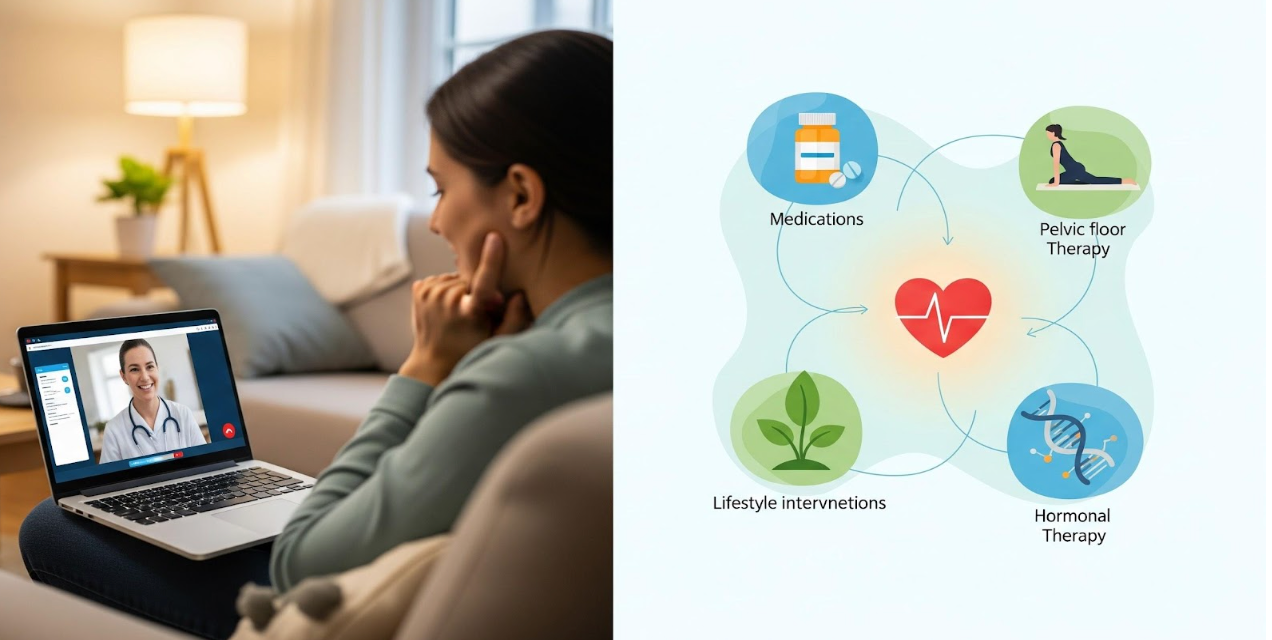

Conclusion
Sexual dysfunction is common and often linked to treatable physical, hormonal, or vascular changes. Understanding the underlying causes helps providers create effective, personalized treatment plans. With the right testing and medical support whether hormonal therapy, medications, pelvic floor therapy, or lifestyle interventions most individuals can significantly improve their sexual health and overall quality of life.
If you are experiencing symptoms affecting your sexual well-being, a telehealth provider can help you get a diagnosis and start the right treatment from the privacy of your home.