GLP-1 Medications: How They Work, Who Needs Them, and What’s New in 2025
In recent years, GLP-1 medications have become a true game-changer in managing obesity, Type 2 diabetes, and metabolic health. These innovative treatments work by mimicking a natural hormone in the body that helps control blood sugar and appetite.
Through my experience working with over a thousand weight loss patients, I’ve witnessed how the right use of GLP-1s can lead to remarkable improvements not just in weight loss but also in overall energy, mood, and long-term health. This article offers a clear look into how GLP-1 medications work, who can benefit from them the most, and what new insights 2025 brings to ensure safe and effective results for every patient.
Key highlights:
How Semaglutide and Tirzepatide Work Compared to Natural GLP-1
- Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy) and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Zepbound) are not the same as the natural hormones your body produces — but they are designed to act like them. Specifically, these medications mimic hormones called GLP-1 (and in Tirzepatide’s case, also GIP) that are naturally released after eating to help regulate blood sugar and appetite.
- The
natural version of GLP-1, produced by specialized intestinal L-cells, doesn’t stay in the body for long — it’s broken down within
1–2 minutes after being released, which makes its effect short-lived.
However, Semaglutide and Tirzepatide are chemically modified to last much longer — about one week per dose.
They achieve this by resisting breakdown by the enzyme DPP-4 (dipeptidyl peptidase-4), allowing continuous GLP-1 receptor activation between injections and providing steady support for blood sugar control and appetite regulation. - The levels of GLP-1–like activity achieved with these medications are much higher and more sustained than what your body naturally produces after a meal. This prolonged activation helps explain why these medications are so effective for Type 2 diabetes, weight loss, and other potential benefits being studied — including cardiovascular and liver protection.
- Importantly, there is
no evidence in current medical research that
exogenous GLP-1 receptor agonists (such as Semaglutide) or
dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonists (such as Tirzepatide)
suppress the body’s own GLP-1 or GIP production — either during treatment or after discontinuation.
In fact, studies of long-term GLP-1 therapy (for example, with Liraglutide) show that natural GLP-1 secretion in response to food may actually increase, not decrease, over time.
To sum it up:
These medications provide your body with
long-acting, consistent GLP-1 support that far exceeds what your gut naturally produces.
That’s what makes them so powerful — and why they only need to be taken
once a week.
Additionally, they
do not suppress your body’s natural GLP-1 and GIP production; they may even
enhance it.
What Are GLP-1 Medications?
Understanding GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists (short for glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists) and GIP receptor agonists (short for glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) are medications that mimic a natural hormone made in the proximal and distal small intestine. These hormones signal your brain that you’re full, slow how fast your stomach empties, and helps your pancreas release insulin. The result: better blood sugar control and reduced appetite.
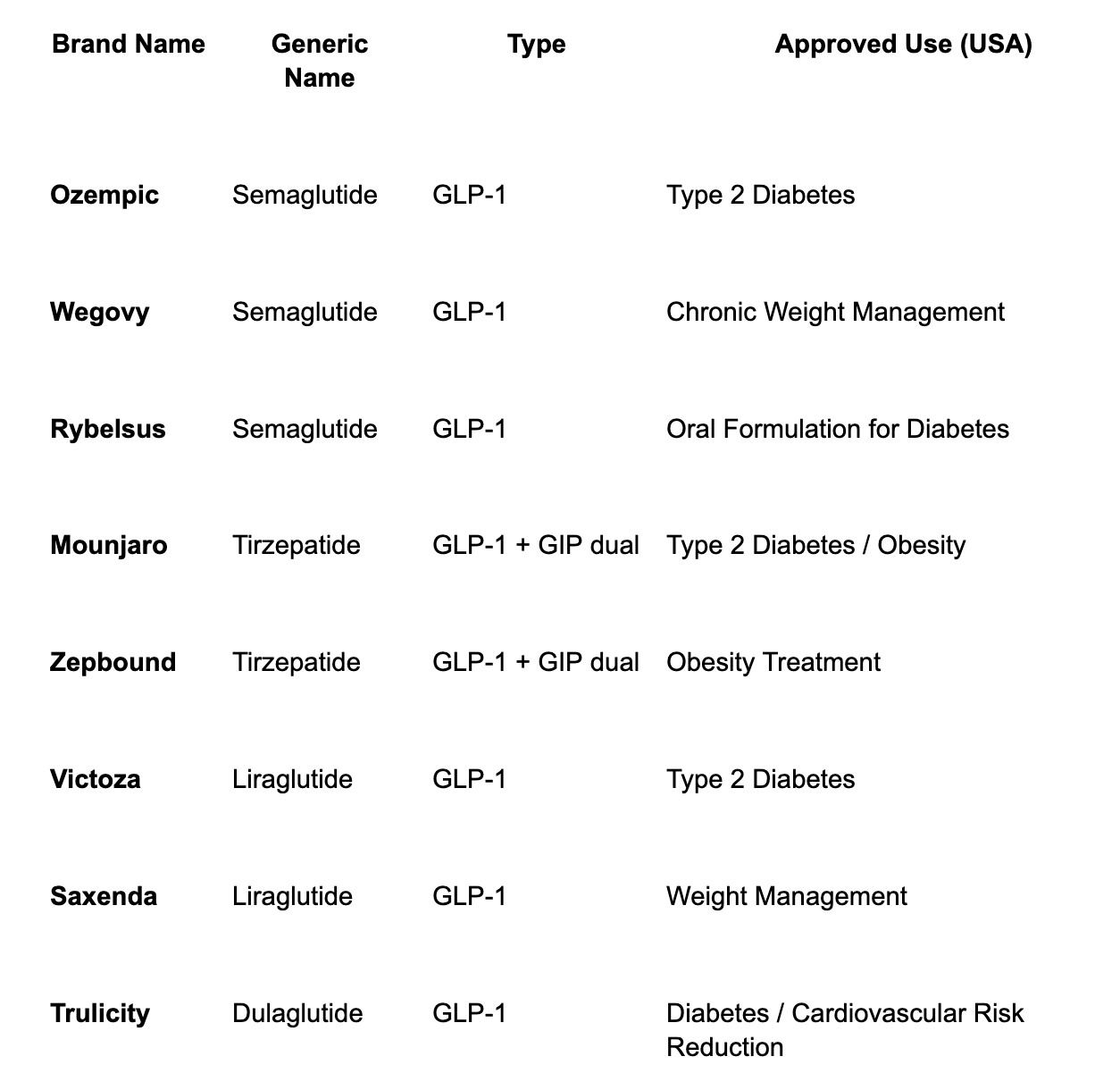
These GLP-1 drugs for weight loss include well-known names such as Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy, Rybelsus), Liraglutide (Victoza, Saxenda), and Dulaglutide (Trulicity). Each works on the same receptor but differs in dosing schedule, absorption, and side-effect profile.
Difference Between GLP-1 and GIP Medications
While GLP-1 acts on one receptor, new drugs combine it with another called GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide). These GLP-1 and GIP dual therapy agents, like Tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Zepbound), work on two gut-hormone pathways at once, offering even greater weight-loss and metabolic improvements. Studies show that patients on Tirzepatide often experience stronger appetite suppression and faster fat loss compared to single-pathway drugs.

How Do GLP-1 Drugs Work?
The Role of GLP-1 in the Body
The hormone GLP-1 naturally helps regulate insulin secretion, blood glucose levels, and appetite. When food enters your gut, GLP-1 signals your pancreas to release insulin and your brain to stop eating. In many people with Type 2 diabetes or obesity, this signaling is blunted. GLP-1 receptor agonists restore that balance, improving satiety and blood-sugar control.
How GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Help With Weight Loss
Patients often ask how a diabetes medication causes such effective weight loss. The key is appetite suppression and gastric emptying delay. When the stomach empties more slowly, you feel full longer and eat less.
Over time, this leads to a meaningful drop in body weight.
In clinical practice, I’ve seen patients lose between 15–30% of their body weight with
Semaglutide or
Tirzepatide, often matching the results of
bariatric surgery alternatives.
GLP-1 and Blood Sugar Control in Type 2 Diabetes
For diabetes management, GLP-1 Medications help lower both fasting and post-meal glucose levels. They protect pancreatic beta cells, reduce hypoglycemia risk, and may even preserve insulin sensitivity over time. Many patients achieve lower A1C without the need for insulin injections.
Who Needs GLP-1 Therapy and Why
GLP-1 therapy is ideal for adults with obesity, Type 2 diabetes, or metabolic conditions like insulin resistance. It also helps people who’ve tried diet and exercise but haven’t achieved lasting results.
These medications may also benefit those with compulsive or binge eating, PCOS, or insulin resistance, by improving appetite control and reducing constant “food noise” — the nonstop thoughts about food and dieting.
GLP-1 for Obesity and Metabolic Health
Beyond weight loss, GLP-1 medications support overall metabolic health. They can improve liver function, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.
Clinical Experience (Doctor’s Insight)
In my practice, treating over 1,000 patients has shown that the best results come when GLP-1 therapy is combined with healthy nutrition, good hydration, and behavioral support.
The main takeaway:
GLP-1 therapy works best alongside lifestyle changes.
Key Benefits of Weight Loss with GLP-1
Improved Liver and Heart Health (MASH, CKD, MACE)
Research confirms that GLP-1 receptor agonists help prevent fatty liver progression and protect the heart. By reducing visceral fat, lowering blood pressure, and improving lipids, they reduce the risk of heart attack and kidney failure. In fact, GLP-1 and stroke risk reduction are now one of the most talked-about benefits in new clinical trials.
Mental and Emotional Health Benefits
Many patients notice improvements in mood, focus, and sleep. This isn’t just from weight loss, it’s part of dopamine and food cravings under GLP-1 therapy, where the brain’s reward system becomes less triggered by junk foods. Emerging data suggest possible neuroprotection and dementia benefits too.
Safety Alerts and FDA Warnings (2025 Updates)

Insights and Pearls from Clinical Practice
Managing Side Effects Effectively
The most common issues I see include gastrointestinal side effects like nausea, constipation, and dehydration and rarely vomiting. Hydration, protein intake, and gradual dose titration help tremendously.
Essential Dietary Tips During GLP-1 Therapy
When taking GLP-1 medications, following proper nutrition and hydration guidelines can help prevent side effects and improve your overall results. Here are the most important recommendations:
- Stay Hydrated
Aim for 2–3 liters (66–99 ounces) of fluids daily. Adequate hydration prevents kidney injury from dehydration, which can easily occur when you’re eating less. - Prioritize Protein Intake
Consume about 1.5 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day.
Example: A person weighing 200 pounds (90.7 kg) should aim for approximately 136 grams of protein daily. Protein supports muscle maintenance and keeps you fuller for longer. - Increase Fiber Consumption
Try to get at least 25 grams of fiber per day. When fat breaks down, it releases stored toxins. Fiber binds to these toxins and helps your colon eliminate them naturally, supporting detoxification and gut health. - Maintain Electrolyte Balance
GLP-1 medications lower insulin levels, which supports weight loss but also causes the kidneys to excrete more salt and water. This can lead to mild dehydration and lower energy due to sodium loss.
To counter this, take a small amount of salt first thing in the morning or include electrolyte-rich fluids in your routine to help boost your energy levels.
Managing Common Side Effects:
Even with proper diet and hydration, mild side effects may occur. These can often be managed through simple adjustments:
- Nausea: Try over-the-counter remedies, ginger or peppermint tea, or ondansetron (if prescribed). Reducing dietary fat earlier in the week of your injection may also help.
- Constipation: Manage it with fiber-rich foods, stool softeners, stimulant laxatives, prunes, or senna tea.
- Belching and Bloating: Gentle clockwise stomach massage, simethicone (Gas-X), and avoiding carbonated beverages can provide relief.
Common Myths About GLP-1 Medications
A common myth is that GLP-1 drugs cause muscle loss. In fact, with adequate protein and regular resistance training, muscle preservation during weight loss is achievable.
Another misconception is that all weight returns after stopping treatment. While some regain can occur,
patients who maintain healthy habits often keep significant results. Correcting
hormonal and nutritional imbalances also supports a smoother transition off medication.
What I’ve Learned from My Patients
Each person’s GLP-1 journey is unique. Those who combine chrononutrition, intermittent fasting, and a whole-food, low–ultra-processed diet experience better outcomes and fewer side effects. Addressing vitamin D deficiency, reducing sucralose intake, and focusing on metabolic balance further enhance long-term success.
Latest News and Research Updates
GLP-1 and Dementia Reduction
A 2025 study suggests GLP-1 therapy may reduce dementia risk. Regular Semaglutide and Tirzepatide use lowered neurodegeneration markers and improved brain resilience in older adults.
GLP-1 and Cardiometabolic Health
Recent meta-analyses show these medications protect against heart disease, CKD, and stroke, expanding their benefits beyond blood sugar control.
Dietary Factors: Chronotype Diet, UPF, and Sucralose
Eating in sync with your sleep cycle and reducing ultra-processed foods enhance GLP-1 effectiveness. Studies also show sucralose may delay satiety, suggesting artificial sweeteners can hinder progress.
Emerging Therapies and FDA Updates
Next-generation treatments like oral dual agonists and dopamine-modulating GLP-1 combos are on the way. The FDA is reviewing updates for Semaglutide use in pregnancy and global cost differences. The upcoming Retatrutide, a triple agonist, is expected to launch soon.
Final Thoughts
The future of GLP-1 and GIP therapies looks promising. Their benefits now extend beyond weight loss, supporting metabolic health, brain protection, and behavioral improvement.
Personalized care remains key, with the right nutrition, monitoring, and medical guidance, patients can achieve safe, lasting weight loss and better overall health.
FAQs:
1. What is the difference between GLP-1 and Ozempic?
GLP-1 refers to a class of medications that mimic the body’s natural glucagon-like peptide-1 hormone, helping control blood sugar and appetite. Ozempic is one specific GLP-1 medication brand (semaglutide) used to treat type 2 diabetes and support weight loss. In short, Ozempic is part of the larger GLP-1 family of drugs.
2. What are GLP-1 medications?
GLP-1 medications are prescription drugs that help regulate blood sugar, reduce appetite, and support weight loss. They work by mimicking the GLP-1 hormone, which increases insulin release and slows digestion, helping patients feel full longer. These drugs are often used for managing obesity and type 2 diabetes.
3. Which GLP-1 medication is best for weight loss?
Among the popular options, Wegovy (semaglutide) and Zepbound (tirzepatide) are considered highly effective for weight loss. Clinical studies show that they can help patients lose a significant percentage of body weight when combined with a healthy lifestyle and medical supervision.
4. How much do GLP-1 medications cost?
The cost of GLP-1 drugs varies depending on the brand and dosage. Without insurance, prices can range from $900 to $1,400 per month. Some insurance plans cover a portion of the cost, and manufacturer savings programs or telehealth services may also help reduce the price. Compounding pharmacies offer pricing starting around $300 for semaglutide and $400 for tirzepatide.
5. What are the common side effects of GLP-1 medications?
Most people tolerate GLP-1 drugs well, but some may experience nausea, vomiting, bloating, constipation, belching or mild stomach discomfort in the first few weeks. These side effects usually lessen over time. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and stay hydrated while using GLP-1s.
6. Are there GLP-1 supplements or pills available?
Currently,
GLP-1 is available as injectable medications and some oral versions, like
Rybelsus (semaglutide oral tablets). While certain supplements claim to “boost GLP-1 naturally,” only prescription medications have proven medical effects. Always consult your doctor before starting any
GLP-1 oral solution or pill. Compounding pharmacies do offer oral lozenges of semaglutide and tirzepatide.